Heliophysics
Written on January 13, 2026 January 13th, 2026 by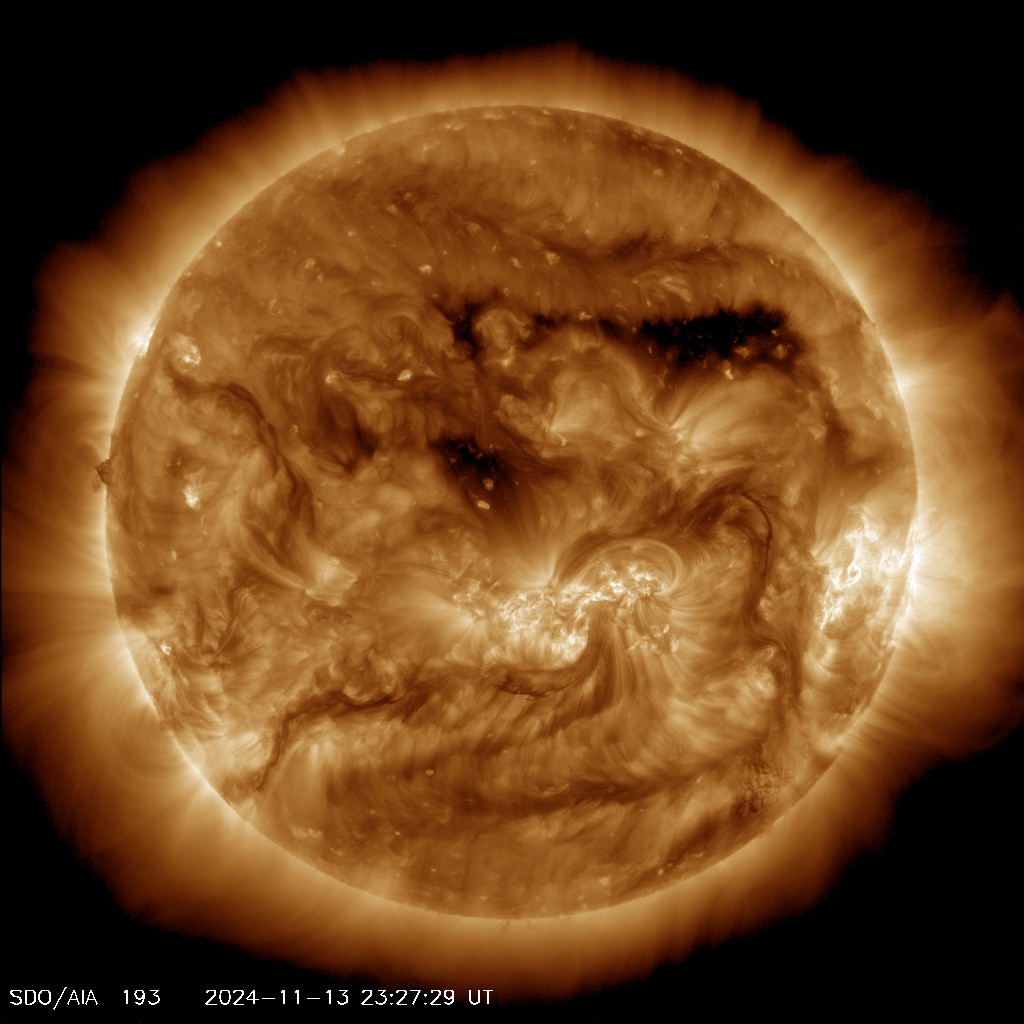
by
tags: covid 13 January 2026Heliophysics
The Science Mission Directorate Heliophysics Division studies the nature of the Sun, and how it influences the very nature of space
Stereo
@nasa-jpl @blackgirlscode its back up but with a warning @whitehouse
We expect the stereo.gsfc.nasa.gov web site to be decommissioned early in 2026. With a few exceptions for out-of-date material, all resources have been copied to https://stereo-ssc.nascom.nasa.gov/ . Please change any bookmarks or automatic downloads you may have set up. https://stereo.gsfc.nasa.gov/ @JHUAPL @CityOflosangeles KarenBass Kamlager Dove @la-county-isd
@usgs @usnavy @nasa-jpl the site for stereo is not responding! Im using the general population lab at BillieJeanKingLibrary @Nasa-develop hi @blackgirlscode @nasa-giss @emit-sds @podaac - Rashard
This site can’t be reached
The webpage at https://stereo.gsfc.nasa.gov/ might be temporarily down or it may have moved permanently to a new web address.
ERR_TUNNEL_CONNECTION_FAILED
External ip = 205.154.246.79 - whatismyipaddress.cOm
Decimal:3449484879
Hostname:lib-03-subnet-79.rdns.cenic.net
ASN:2152
ISP:CENIC
Services:None detected
Country:United States
State/Region:California
City:Cypress
Latitude:33.8170 (33° 49′ 1.05″ N)
Longitude:-118.0373 (118° 2′ 14.25″ W)
Hinode (Solar-B)
@nasa-pds @nasa-jpl discovered
NASA's Near Space Network
STATION NAME:McMurdo Ground Station
LOCATION:McMurdo, Antarctica
JAN 14 ~07:33 AM NZDT
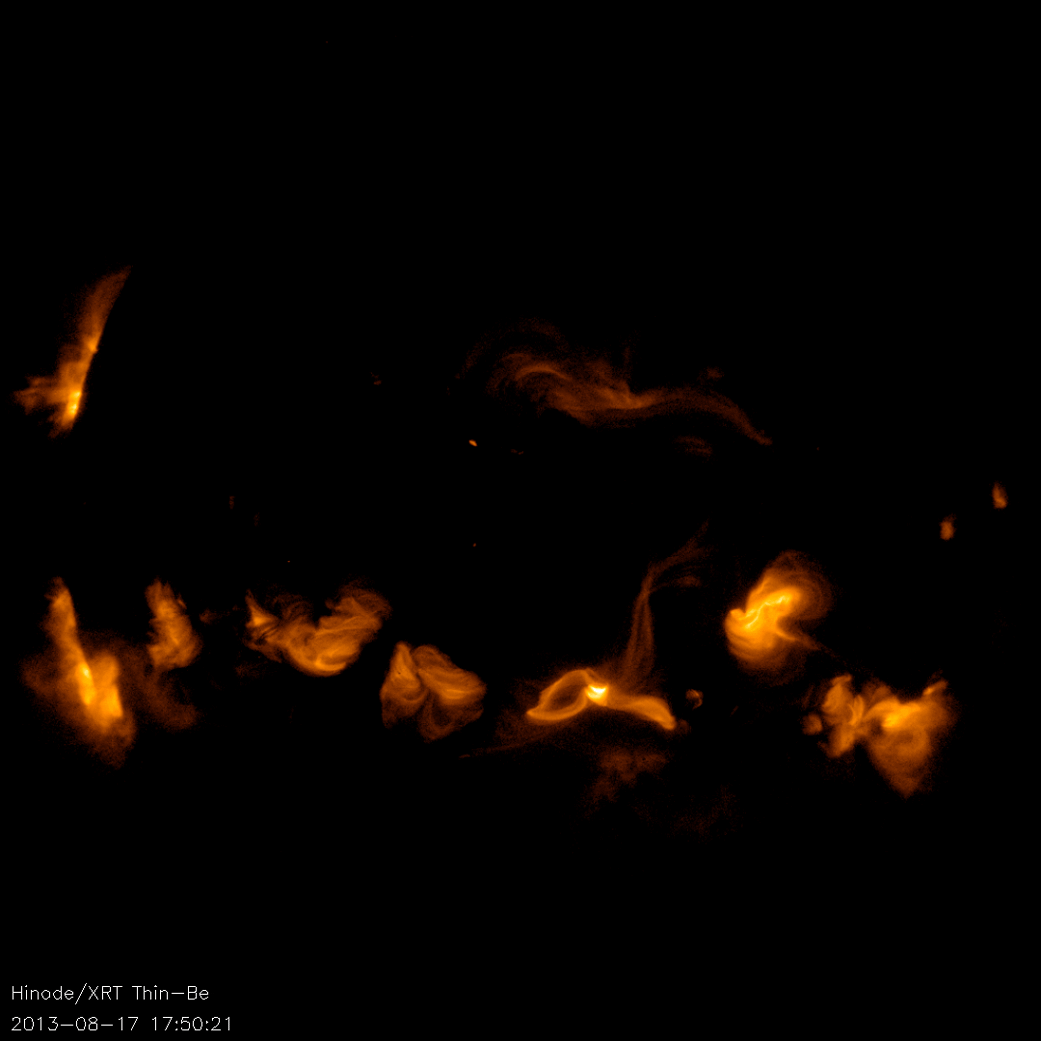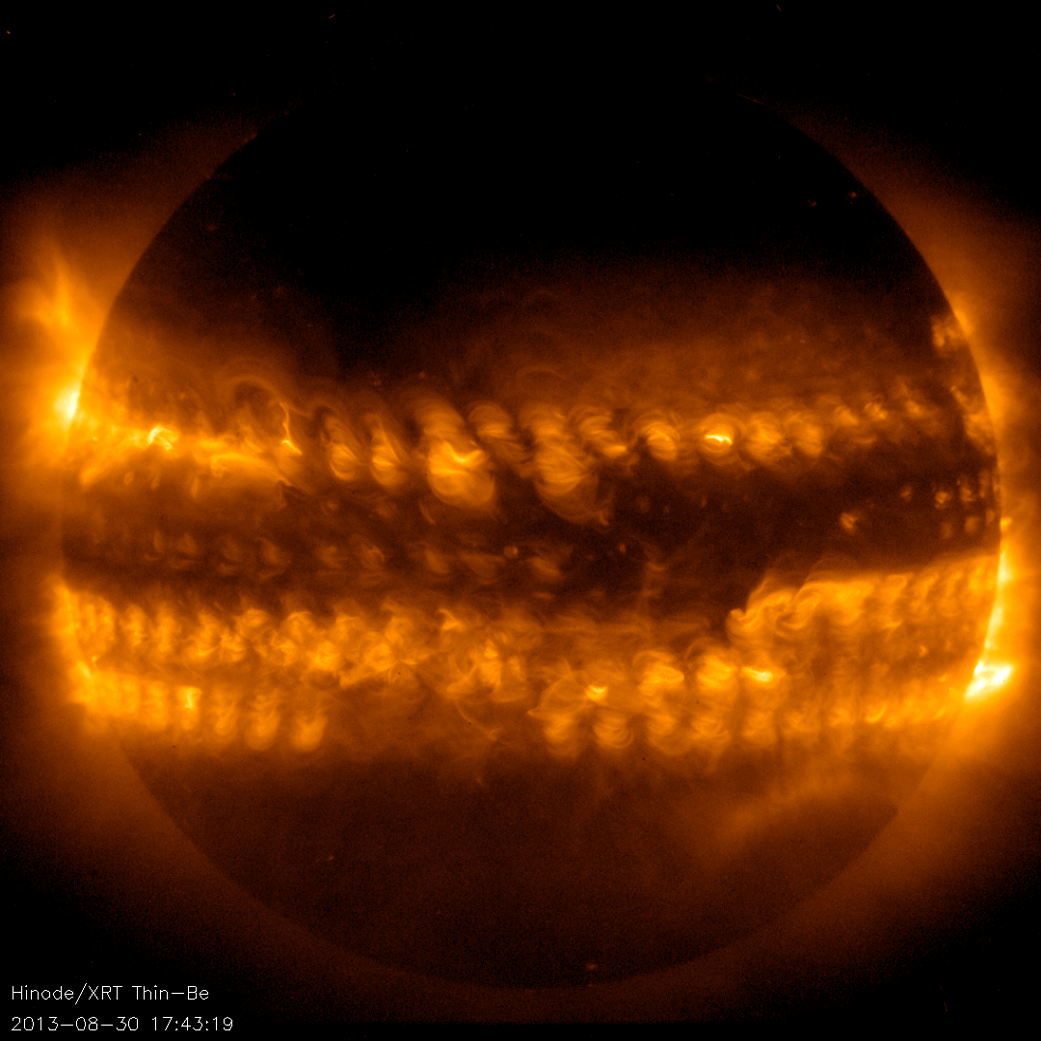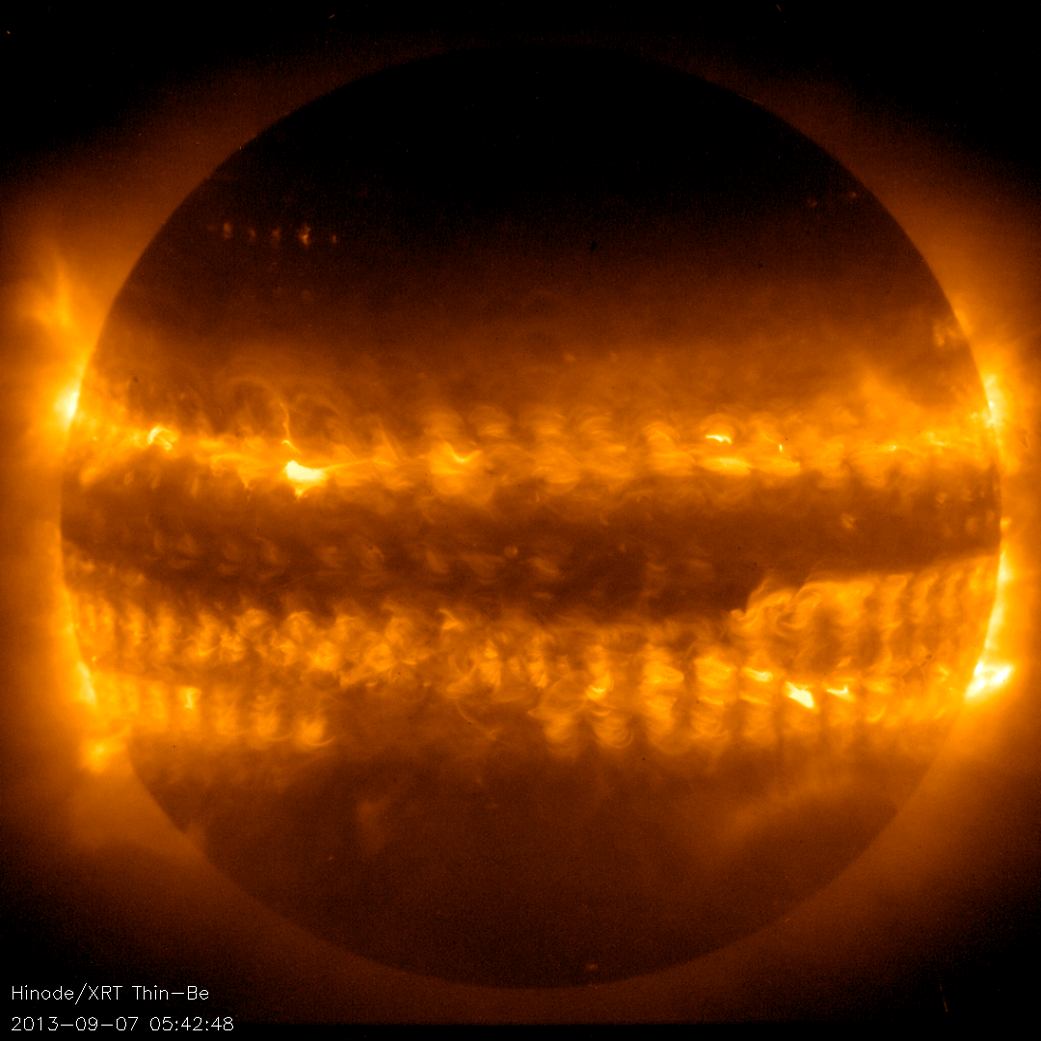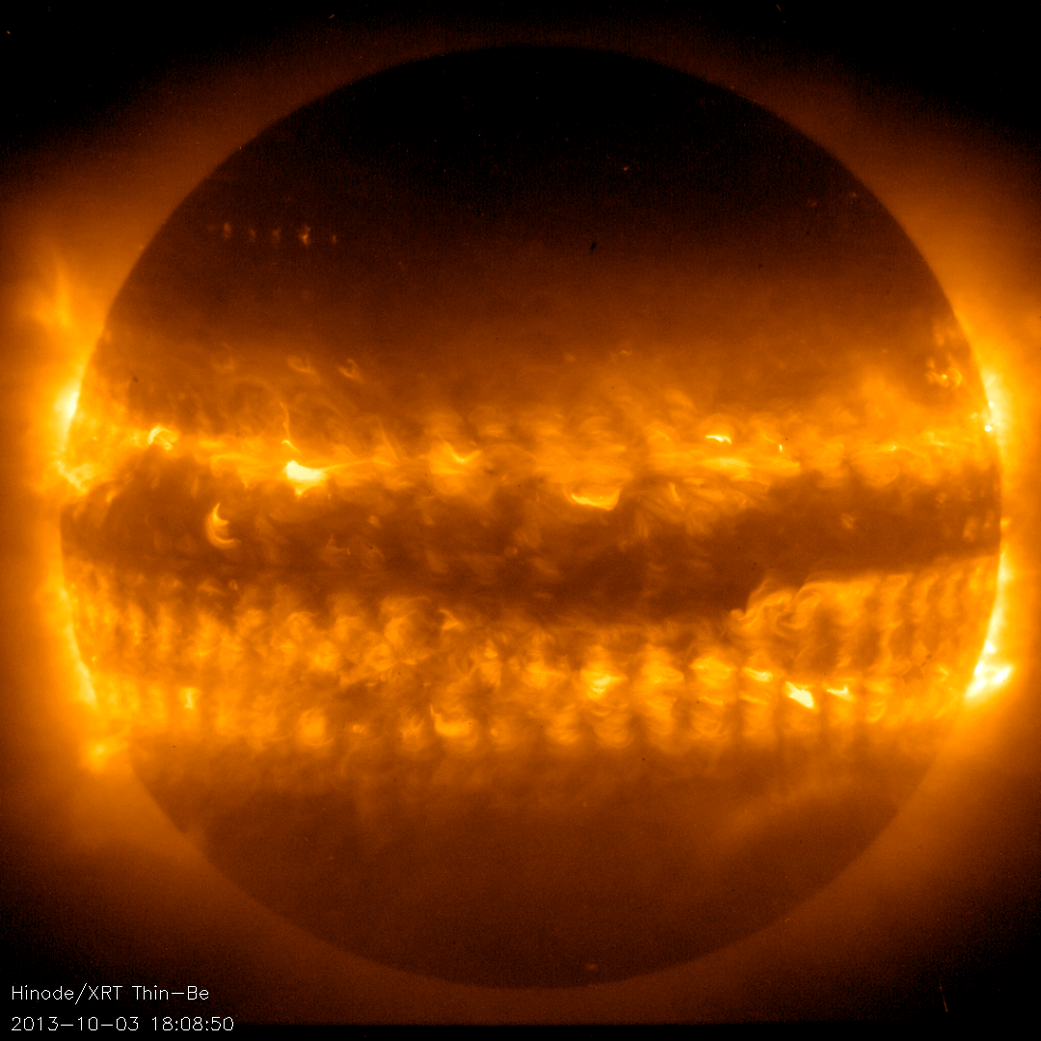
Hinode explores the magnetic fields of the Sun to improve understanding of what powers the solar atmosphere and drives solar eruptions. Hinode’s Solar Optical Telescope is the first space-borne instrument to measure the strength and direction of the Sun’s magnetic field on the Sun’s surface, the photosphere. missionWebfront : images @la-county-isd Karen Bass HollyJMitchell HildaSolis JAnice HAhn, I found another heliophysics mission @nasa-jpl @nasa-pds, it popped up in the NearSpaceNEtwork_MonitoringTool SCAN @blackgirlscode thethings that pop up in the monitoring tools are good things to use as ideas for managing a databese… safe content
About the SOHO Mission
SOHO, the Solar & Heliospheric Observatory, is a project of international collaboration between ESA and NASA to study the Sun from its deep core to the outer corona and the solar wind.
SOHO was launched on December 2, 1995. The SOHO spacecraft was built in Europe by an industry team led by prime contractor Matra Marconi Space (now EADS Astrium) under overall management by ESA. The twelve instruments on board SOHO were provided by European and American scientists. Nine of the international instrument consortia are led by European Principal Investigators (PI’s), three by PI’s from the US. Large engineering teams and more than 200 co-investigators from many institutions supported the PI’s in the development of the instruments and in the preparation of their operations and data analysis. NASA was responsible for the launch and is now responsible for mission operations. Large radio dishes around the world which form NASA’s Deep Space Network are used for data downlink and commanding. Mission control is based at Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland.
Further information about SOHO: PDF @nasa=pds @blackgirlscode
IRIS
Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph
 hi coral
[added 1/6/25] @nasa-jpl @nasa-pds hi @blackgirlscode link
hi coral
[added 1/6/25] @nasa-jpl @nasa-pds hi @blackgirlscode link
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe Discovers Natural Radio Emission in Venus’ Atmosphere
On a mission to “touch the Sun,” NASA’s Parker Solar Probe became the first spacecraft to fly through the corona – the Sun’s upper atmosphere – in 2021,During a brief swing by Venus, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe detected a natural radio signal that revealed the spacecraft had flown through the planet’s upper atmosphere.

Bepi Columbo @nasa-pds @blackgirlscode Horizons Results @nasa API SOURCE: NASA/JPL Horizons API
Page up
JPL Horizons, version 4.98d
Type '?' for brief help, '?!' for details,
'-' for previous prompt, 'x' to exit
System news updated August 7, 2025
Horizons> epic
*******************************************************************************
Revised: Sep 03, 2025 BepiColombo / (Sun) -121
http://sci.esa.int/bepicolombo/
JPL Horizons, version 4.98d
Type '?' for brief help, '?!' for details,
'-' for previous prompt, 'x' to exit
System news updated November 13, 2025
Horizons> hinode
>EXACT< name search [SPACE sensitive]:
NAME = hinode;
Continue [ <cr>=yes, n=no, ? ] :
*******************************************************************************
JPL/DASTCOM Small-body Index Search Results 2026-Jan-13 10:36:38
Comet AND asteroid index search:
NAME = hinode;
Matching small-bodies:
No matches found.
*******************************************************************************
Select ... [F]tp, [M]ail, [R]edisplay, ?, <cr>: hi
*******************************************************************************
Multiple major-bodies match string "HI*"
ID# Name Designation IAU/aliases/other
------- ---------------------------------- ----------- -------------------
506 Himalia JVI
558 Philophrosyne 2003J15 JLVIII 55067
627 Skathi 2000S8 SXXVII
637 Bebhionn 2004S11 SXXXVII 65039
663 Thiazzi 2004S33 65075
814 Hippocamp 2004N1
-75 OMOTENASHI (spacecraft) 2022-156D
-235 STEREO-B (spacecraft) 2006-047B BEHIND
-234900 STEREO Third Stage (spacecraft) 2006-047C
-134381 Kepler Booster (Third Stage) (space2009-011B
-140267 Himawari-8 (spacecraft) 2014-060A
-141836 Himawari-9 (spacecraft) 2016-064A
120136108 Hi'iaka Haumea I
Number of matches = 13. Use ID# to make unique selection.
*******************************************************************************
Select ... [F]tp, [M]ail, [R]edisplay, ?, <cr>: -235
*******************************************************************************
Revised: Feb 08, 2023 STEREO-B Spacecraft -235
http://stereo.gsfc.nasa.gov/
NOTE:
Contact with STEREO-B was lost 2014-Oct-01.
After 22 months, contact was regained at 22:27 UTC on August 21, 2016, when
the Deep Space Network established a lock on STEREO-B for 2.4 hours. The
trajectory here is updated to use that tracking data.
It has been determined the spacecraft is in an uncontrolled spin of
3 deg/second.
2023-Feb-08:
There has been no contact or new tracking data since 2016, but an updated
prediction was added to support a search effort.
2017-Sep-20:
Fix did NOT occur. Last contact with the spacecraft was September 23, 2016.
2016-Oct-14:
Another opportunity to potentially fix the spacecraft will not occur until
mid-2017. Once its computer is powered on there will be about two minutes
to upload the fix before STEREO-B enters failure mode again.
http://stereo-ssc.nascom.nasa.gov/behind_status.shtml
BACKGROUND:
STEREO (Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory) is the third mission in
NASA's Solar Terrestrial Probes program (STP). This two-year mission will use
two nearly identical space-based observatories - one ahead of Earth in its
orbit, the other trailing behind - to provide stereoscopic measurements to
study the Sun and the nature of coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
OBJECTIVES:
* Understand the causes and mechanisms of coronal mass ejection (CME)
initiation.
* Characterize the propagation of CMEs through the heliosphere.
* Discover the mechanisms and sites of energetic particle acceleration in
the low corona and the interplanetary medium.
* Improve the determination of the structure of the ambient solar wind.
SPACECRAFT:
Launch (Delta II 7925-10L) = October 26, 2006 @ 1:53
Mission end = 2 year nominal mission after launch
Dimensions = 1.14m x 1.22m (launch), 6.47m x 2.03m (deployed)
Launch Mass = 620 kg (includes propellant)
Power consumption = 475 watts
Data downlink = 720 kilobits/sec
Memory = 1 GB
Attitude = control within 7", knowledge within 0.1"
INSTRUMENTS (4 packages on each spacecraft):
* Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI)
* STEREO/WAVES (SWAVES) radio burst tracker
* In-situ Measurements of Particles and CME Transients (IMPACT)
* PLAsma and SupraThermal Ion Composition (PLASTIC)
ORBIT:
STEREO-A and STEREO-B will be launched together, then separate. The Moon's
gravity will be used to redirect the observatories to their appropriate
orbits, something the launch vehicle alone is not able to do.
For the first three months after launch, the two observatories will fly in
highly elliptical orbits extending from very close to Earth to just beyond
the Moon's orbit. STEREO Mission Operations personnel at APL will
synchronize spacecraft orbits so that about two months after launch they
encounter the Moon, at which time one of them is close enough to use the
Moon's gravity to redirect it to a position "ahead"/leading the Earth.
Approximately one month later, the second observatory will encounter the
Moon again and be redirected to its orbit "behind"/trailing the Earth.
POST-LAUNCH SPACECRAFT TRAJECTORY
Merged segments, includes 2016-Aug-21 recovery tracking data update,
with long-term predictions after 2016-Sep-12:
Trajectory name Start Stop
------------------------------------- ----------- -----------
concatenated DEPM trajectory segments 2006-Oct-26 2014-Sep-28
235_120day_20140928_01.V0.2 2014-Sep-28 2014-Nov-25
235_120day_20141125_01.V0.2 2014-Nov-25 2015-Jan-01
235_1461day_20150101_01.V0.2 2015-Jan-01 2015-Jul-16
235_1460day_20150716_01.V0.2 2015-Jul-16 2016-Jan-29
235_5295day_20160129_01.V0.5 2016-Jan-29 2016-Aug-21
behind_2016_256_01.depm 2016-Aug-21 2016-Sep-12
235_5295day_20160129_01.V0.5 2016-Sep-12 2020-Oct-27
235_baseline_1460day_20201027_01 2020-Oct-27 2024-Oct-26
******************************************************************************
Select ... [E]phemeris, [F]tp, [M]ail, [R]edisplay, ?, <cr>:
layout: default title: HoleToAnotherUniVersE